A recent research paper “Advancing Food Safety Through IoT Real-Time Monitoring & Control System in Food Production” talks about how introducing an IoT-based system for real-time monitoring of critical food safety parameters such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of pathogens can continuously monitor environmental conditions and potential hazards throughout the food supply chain. Let’s dive deeper into what this concept constitutes for food businesses to transform the way production operations are managed.
Growing Significance of IoT Technology for Advancing Food Safety
The global food industry still grapples with substantial challenges in maintaining food safety across the supply chain with conventional monitoring and control methods often failing to provide real-time insights, resulting in inefficiencies, delayed responses to probable risks, and heightened risks of contamination. Furthermore, manual processes are susceptible to human error, compounding these issues. IoT technology, with its ability to provide real-time data and insights, presents a compelling solution to these challenges, emerging as a game-changer in the field of food safety management.
How IoT-Powered Food Safety Works
IoT-powered food safety solutions operate by connecting a network of smart sensors and devices that continuously monitor critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, pH levels, and more. These sensors can be deployed throughout the food supply chain, from farms and processing plants to transportation, storage, and retail. The data collected by these sensors is transmitted in real-time to a central platform, where it is analyzed and used to make informed decisions.
Key Components of an IoT-Powered Food Safety System
Smart Sensors: The backbone of any IoT-powered system, smart sensors continuously monitor key variables that impact food safety. For example, temperature sensors in a cold storage facility can detect fluctuations that might indicate a malfunction in the refrigeration system, allowing for immediate corrective action.
Connectivity: IoT systems rely on robust connectivity, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks, to transmit data from sensors to the central platform. This ensures that the data is available in real time, enabling quick responses to any issues.
Data Analytics: The real power of IoT lies in its ability to process and analyze large volumes of data. Advanced analytics can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and predict potential problems before they occur, allowing for proactive management of food safety.
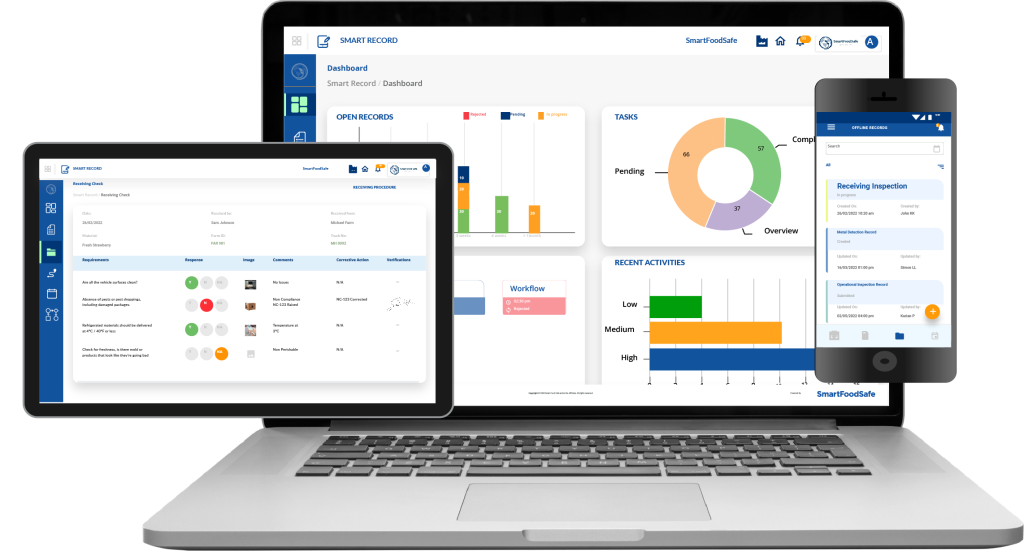
User Interface: The data collected by the system is presented to users through an intuitive interface, such as a dashboard or mobile app. This allows users to monitor the entire supply chain at a glance and receive alerts when action is needed.
Automation and Control: Some IoT-powered systems can automate responses to certain conditions. For example, if a sensor detects that the temperature in a storage unit is rising above safe levels, the system could automatically adjust the cooling system or notify maintenance personnel to investigate.
Benefits of IoT-Powered Food Safety
The adoption of IoT-powered food safety solutions offers numerous benefits that make it a game-changer for the industry.
-
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
One of the most significant advantages of IoT-powered food safety is the ability to monitor critical parameters in real time. Unlike traditional methods that rely on periodic checks, IoT systems provide continuous monitoring, allowing for immediate detection of any issues. This real-time data enables quick responses to potential safety hazards, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses and product recalls.
For example, if a temperature sensor in a refrigerated truck detects that the temperature is rising above the safe threshold, the system can immediately alert the driver and fleet manager. This allows for prompt action to be taken, such as adjusting the temperature or transferring the goods to another vehicle, before the food is compromised.
-
Enhanced Traceability
Traceability is essential for maintaining food safety and meeting regulatory requirements. In the event of a contamination issue, it is crucial to quickly identify the source and prevent further distribution of affected products. IoT-powered systems provide end-to-end traceability, allowing companies to track food products from farm to fork.
With real-time data collection, companies can quickly identify the origin of any safety issue, whether it’s a contaminated batch of raw ingredients or a malfunction in a processing plant. This not only helps contain the problem but also minimizes the economic impact by avoiding widespread recalls.
-
Predictive Maintenance
IoT systems do more than just monitor current conditions; they also predict potential issues before they occur. By analyzing data from sensors, IoT-powered software can identify patterns that suggest equipment is likely to fail. For instance, if a refrigeration unit’s temperature fluctuates more than usual, the system might predict a compressor failure and schedule maintenance before the unit breaks down completely.
This predictive capability helps prevent costly downtime and ensures that food remains safe throughout the supply chain.
-
Compliance and Reporting
Food safety regulations are becoming more and more stringent worldwide. Compliance with these regulations requires meticulous record-keeping and reporting, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors when done manually. IoT-powered food safety systems automate this process, ensuring that all data is accurately recorded and easily accessible for audits and inspections.
Automated reporting not only saves time but also ensures that companies remain compliant with local, national, and international food safety standards. This is where Smart Food Safe’s Smart Record software shines, offering seamless integration with IoT systems to provide comprehensive, automated record-keeping and compliance management.
-
Cost Efficiency
While the initial investment in IoT technology may seem high, the long-term cost savings are significant. By preventing food spoilage, reducing recalls, and minimizing downtime, IoT-powered systems help companies save money and protect their brand reputation. The ability to optimize processes and improve efficiency can lead to lower operational costs.
Real-World Applications of IoT in Food Safety
The impact of IoT-powered food safety systems can be seen across various sectors of the food industry.
- Agriculture – IoT sensors in agriculture can monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health in real time. This data helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting, ensuring that crops are grown under optimal conditions. IoT systems can track the use of pesticides and other chemicals, helping to ensure that food products are safe and comply with regulatory standards.
- Food Processing – In food processing plants, IoT sensors monitor equipment and environmental conditions to ensure that food products are handled safely. For example, sensors can detect the presence of pathogens in processing equipment or monitor the temperature of cooking processes to ensure that food is cooked to the appropriate temperature to kill harmful bacteria.
- Cold Chain Management – Maintaining the cold chain is critical for the safety of perishable food products. IoT-powered systems provide real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity levels throughout the cold chain, from production to distribution to retail. This ensures that perishable goods remain within safe temperature ranges, reducing the risk of spoilage and contamination.
- Retail and Restaurants – In retail stores and restaurants, IoT sensors can monitor the temperature of refrigerators and freezers, ensuring that food products are stored at the correct temperatures. IoT systems can track the freshness of food products and automatically remove items that are past their expiration date, reducing waste and ensuring that customers receive fresh, safe food.
Challenges in Implementing IoT-Based Food Safety Systems & How to Address Them
Organizations face formidable challenges when seeking to integrate IoT technologies into their supply chains. By identifying and addressing these obstacles, given below is a comprehensive understanding of the practical roadblocks and issues that must be navigated to harness the full potential of IoT within the food safety management system:
A. Enhancing Data Security and Privacy
Challenge: IoT devices in food safety systems collect and transmit sensitive data, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks.
Resolution: Implement robust encryption and secure transmission protocols to protect data. Deploy strong authentication mechanisms to control access, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations to safeguard individual privacy.
B. Improving Interoperability
Challenge: The lack of universal standards leads to communication issues between different IoT devices, resulting in data silos and higher operational costs.
Resolution: Advocate for and adopt universal standards to enable seamless communication between IoT devices. Develop efficient middleware solutions to bridge compatibility gaps, thereby minimizing data silos and enhancing operational efficiency.
C. Addressing Scalability
Challenge: Managing the high volume and velocity of data generated by IoT devices can overwhelm existing infrastructure.
Resolution: Invest in scalable data infrastructure capable of handling large datasets. Utilize advanced analytics and ensure that specialized skills and resources are available to process and analyze data effectively for actionable insights.
D. Evaluating Costs and ROI
Challenge: Implementing IoT technology involves significant upfront costs and ongoing expenses, making ROI evaluation complex.
Resolution: Conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses considering all associated costs and potential benefits. Quantify both tangible benefits like cost reductions and intangible benefits such as improved decision-making to ensure a favorable return on investment.
E. Managing Change and Developing Workforce Skills
Challenge: Resistance to change and a lack of necessary skills among employees can hinder the effective adoption of IoT systems.
Resolution: Implement comprehensive change management strategies to foster a culture of innovation and adaptability. Provide extensive training programs to equip employees with the skills required to operate and benefit from IoT systems.
F. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Challenge: Navigating the complex web of regulations governing data privacy and product tracking can be challenging.
Resolution: Establish robust data governance frameworks to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Align IoT systems with regulatory requirements and conduct regular audits to avoid legal liabilities and protect the organization’s reputation.
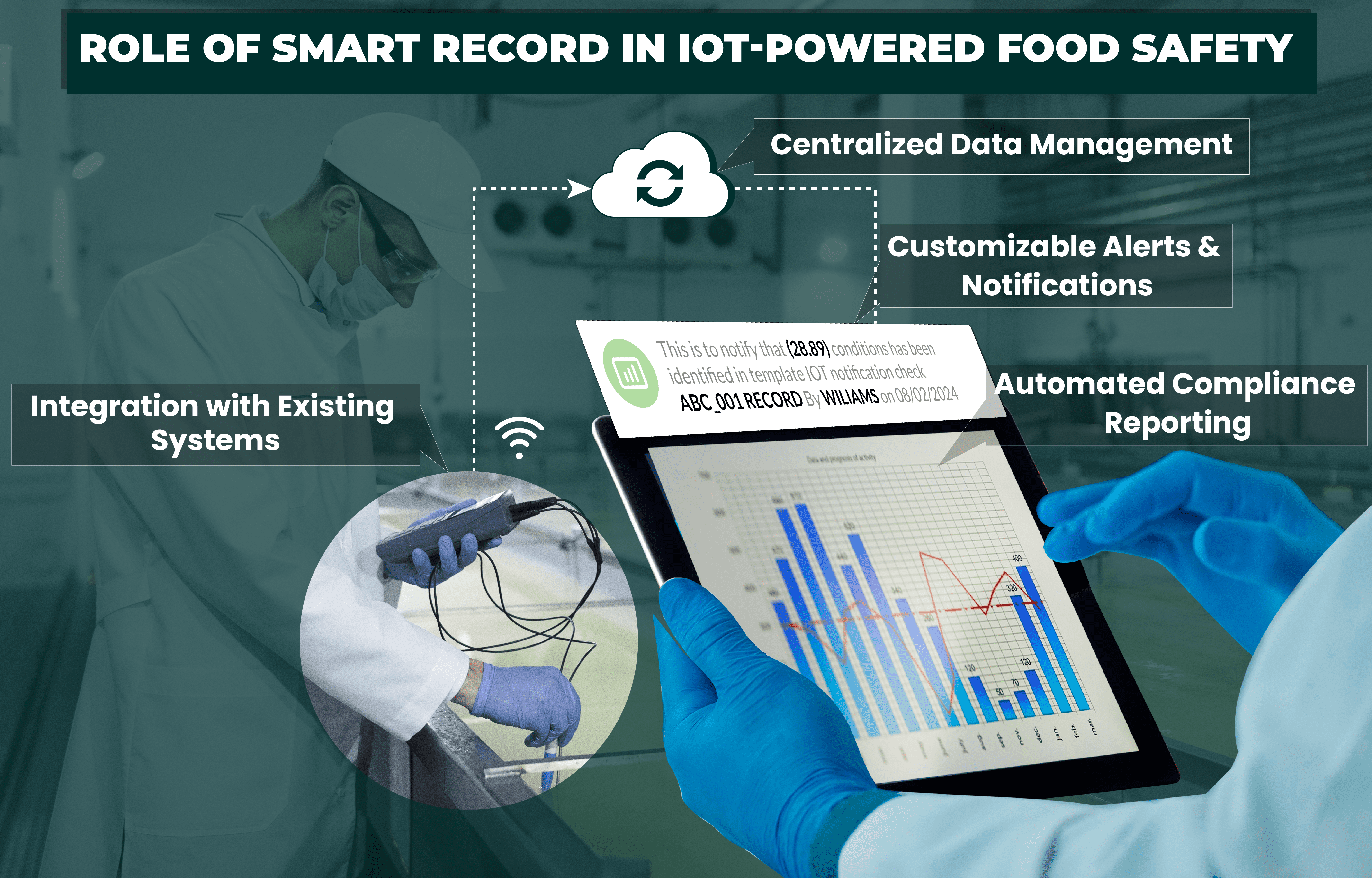
Role of Smart Record in IoT-Powered Food Safety
While IoT-powered systems provide real-time monitoring and control, the data generated needs to be managed effectively to maximize its value. This is where Smart Record comes into play. Smart Record is designed to integrate seamlessly with IoT systems, offering a comprehensive solution for managing food safety data, ensuring compliance, and optimizing operations.
- Centralized Data Management – Smart Record consolidates data from various IoT sensors and devices, and via voice and Bluetooth integration into a single platform, providing an overview of the entire food supply chain. This centralized approach simplifies data management, making it easier to monitor, analyze, and act on critical information. By having all relevant data in one place, food safety professionals can efficiently oversee operations and quickly address any issues that arise.
- Automated Compliance Reporting – With Smart Record, compliance reporting is automated, ensuring that all necessary documentation is accurately recorded and readily available for audits and inspections. This feature reduces the risk of non-compliance, which can lead to costly fines and damage to a company’s reputation. The system also verifies compliance with food safety standards, further minimizing the chances of human error.
- Customizable Alerts and Notifications – Smart Record offers customizable alerts and notifications based on specific criteria. For example, if a temperature sensor detects a deviation from the safe range, the system can immediately notify the relevant personnel. These real-time alerts enable swift corrective actions, ensuring that potential safety issues are addressed before they escalate.
- Integration with Existing Systems – Smart Record’s IoT functionalities are designed to integrate with existing food safety management systems, providing an apt solution that enhances rather than disrupts current operations without requiring an overhaul of existing infrastructure. This flexibility allows companies to adopt Smart Record with ease, optimizing their food safety practices while maintaining operational continuity.
In an industry where consumer trust and brand reputation are paramount, investing in an IoT-powered food safety tool like Smart Record is not just a smart move—it is important for staying competitive and protecting your business in an increasingly complex and demanding landscape.